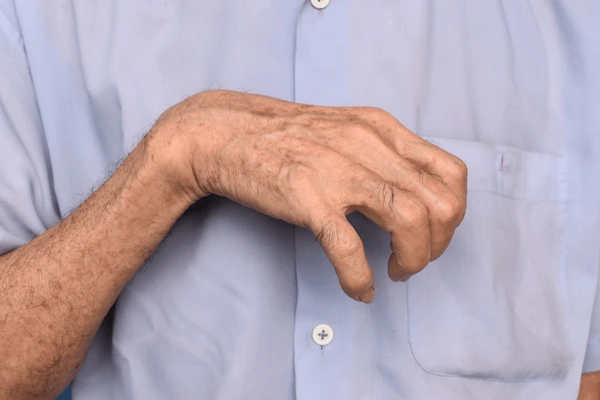
Claw Hand It’s called Ulnar claw hand. Claw hand is an abnormal position that develops due to injury of the ulnar nerve. The Ulnar claw hand occurs more with a low ulnar nerve lesion and typically causing flexion and clawing of the fourth and fifth fingers. Due to the unopposed action of the medial or the ulnar part of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle.
How do you check for clawing?
Clawing is seen when the patient is asked to extend the fingers. A hand in the ulnar claw position will have the fourth and fifth fingers extended at the MCP joint and flexed at the Interphalangeal (IP) joints. The interphalangeal joints.
So when you ask the patient to extend the fingers, the patient will try to extend the fingers, but he will not be able to extend the interphalangeal joints of fingers Number four and number five.
So why this happen? So let’s check the ulnar nerve innervation. The ulnar nerve innervates the ulnar half of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle.
It also innervates the third and fourth lumbrical muscles And all of the interosseous muscles In addition to the abductor pollicis muscle and the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis. So injury of the ulnar nerve at the wrist will lead to loss of function of all the interosseous muscle and the ulnar two lumbricals.
The second and third digits are mainly unaffected by this injury except in abduction and abduction of the fingers, while the fourth and fifth digits are largely affected by injury to the ulnar nerve. With dysfunction of these muscles, the extensor digitorum is unopposed, causing hyperextension of the fourth and fifth digits at the MCP joints. read….. Winged scapula Trapezius Muscle
The extensor digitorum is very effective in extending the MCP joint The extensor digitorum gets help from the interossei and the lumbricals to extend the IP joints through the extensor hood, or the extensor expansion at the interphalangeal joints the IP joints
The extensor digitorum has to overcome and counteract deflection force exerted by the functional flexor digitorum profundus, and clearly the extensor digitorum cannot do it because there is no assistance from the lumbrical or the interossei, and the clawing of the fingers will show up.
This is usually a distal lesion that preserve innervation to the medial or (ulnar half) of the profundus muscle. And in this disillusions, the sensation at the dorsum of four and five fingers will be intact, because the dorsal sensory nerve may be spared if the lesion is at rest. But you will definitely find numbness of the fourth and fifth fingers at the volar aspect .
You may find wasting of the first interosseous muscle. You also may find flattening of the hypothenar eminence. The fourth and fifth fingers will be stuck in a position of hyperextension at the MCP joints, and the hyperflexion at the interphalangeal joints.
Now, if the lesion of the ulnar nerve is high and the flexor digitorum profundus is not working, then there will be no clawing and definitely in high lesion you will have loss of sensation in the dorsal aspect of number four and five fingers.
Differential diagnosis
- volkmann’s ischemic contracture.
- Dupuytren’s contracture.
- Spastic hand.
- Congenital flexion contracture, which is called (camptodactyly)
Claw hand and sign of benediction
Claw hand and sign of benediction may appear similar. However, they are not the same. The claw hand comes from an ulnar nerve injury, usually distal lesion. The Sinopec addiction usually comes from a median nerve injury, usually a high median nerve, or from an anterior interosseous nerve lesion Sinopec addiction is the position of the hand when you ask the patient to make a fist, so the fingers two and three will remain extended When you ask the patient to extend the fingers, they will be able to extend it, but they cannot flex two and three digits and they cannot do the okay sign.
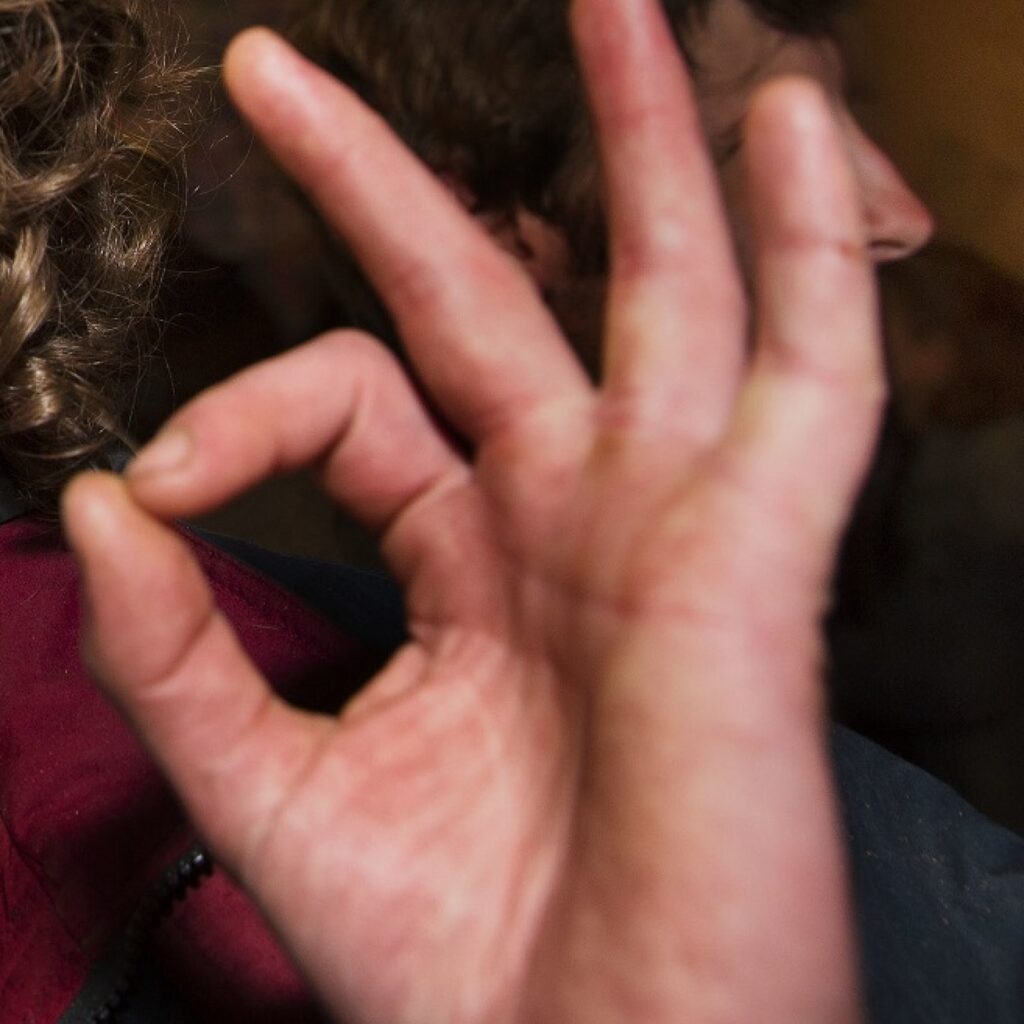

I Can’t Do The OK Sign, What Does it Mean?
If a person cannot do the OK sign, this person may have a nerve injury (anterior interosseous nerve injury) This is the sign of an addiction. When you flex the fingers, two and three fingers will remain extended. It’s a median nerve or anterior interosseous nerve injury. article source click here