Do you know what’s the difference between anatomical dead space and physiological dead space? Welcome to Times For Health’s. Let’s get started.
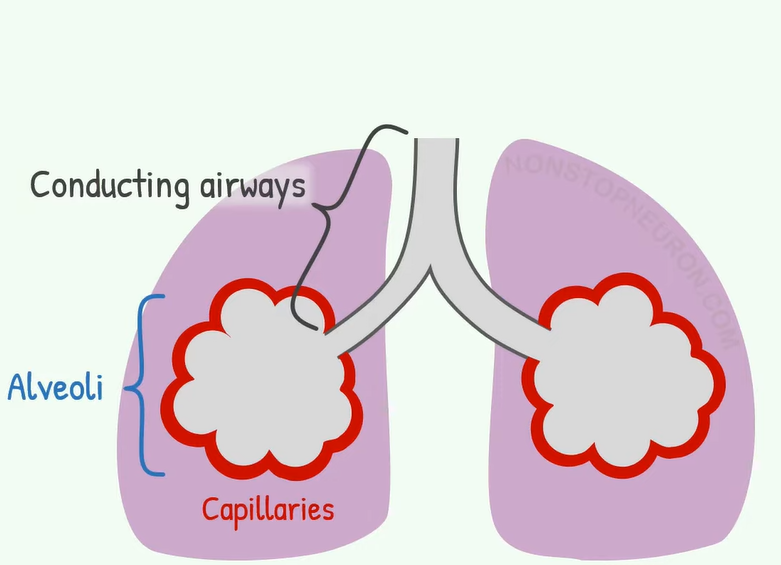
Lung Diagram
This is simplified diagram of lung. This part represents conducting airway It is the passage from nose and lips to just before alveoli. This part does not participate in gas exchange. These are alveoli. And these are pulmonary capillaries supplying alveoli Alveoli participate in gas exchange Now let’s see tidal volume.
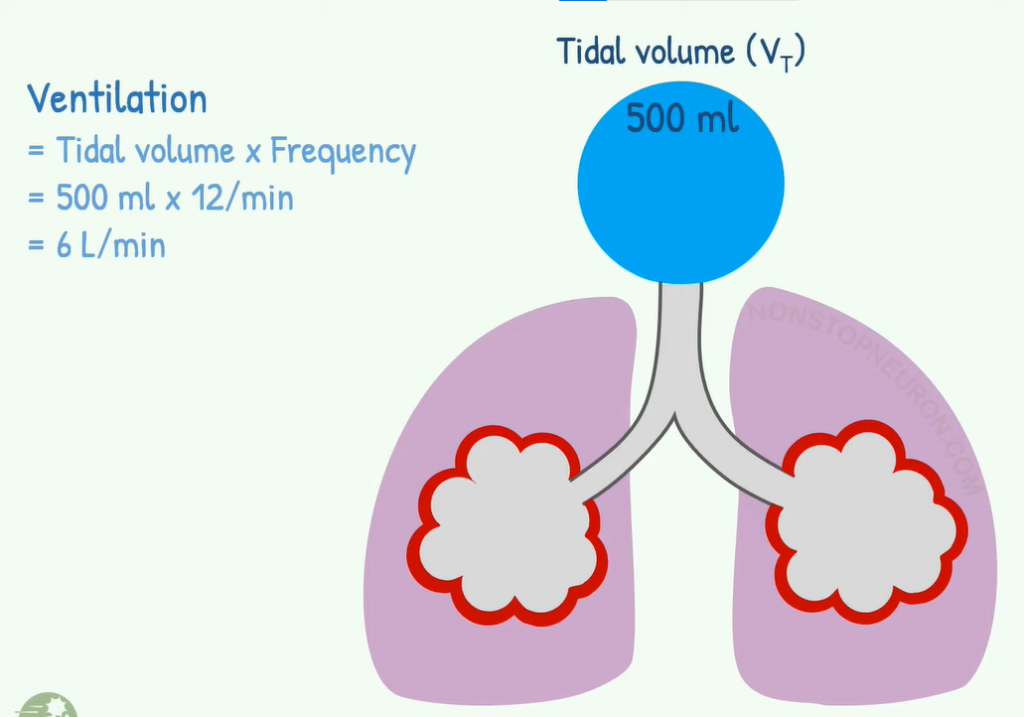
Tidal Volume
It’s the amount of air that we breathe in and out with each respiration Normally it’s about 500ml. In adults Ventilation is the amount of air that moves in and out of lungs in one minute. If we multiply tidal volume with frequency of respiration, we get the value of ventilation Tidal volume of 500ml at 12 breaths per minute gives ventilation six liters per minute.

Alveoli
Now, out of this 500ml air that we breathe in, three 50ml reaches to the alveoli and one 50ml stays in conducting airway Alveolar ventilation is amount of this fresh air entering in the alveoli every minute. So multiplying this three 50ml with 12 breaths per minute gives alveolar ventilation 4.2l per minute. Coming to this one 50ml as it stays in conducting airway, it does not contribute in gas exchange So this phase is called anatomical dead space.
Ventilation of this space is called dead space. Ventilation Anatomical dead space of one 50ml, multiplied by 12 breaths per minute gives dead space ventilation 1.8l per minute. Thus, out of six litres of fresh air that we breathe every minute, only 4.2l enters into the alveoli and is actually useful remaining 1.8l air ventilates the dead space and is not useful in gas exchange.
Please note that I have ignored air that is already there in the airways before starting inspiration to keep the discussion simple
Now there can be one more type of dead space that is alveolar dead space. In some pathological conditions, some alveoli do not receive blood supply They still receive air, but due to lack of blood supply, these alveoli do not contribute in gas exchange. This is called alveolar dead space Physiological dead space is some of anatomical dead space and alveolar dead space.
Healthy person do not have alveolar dead space, so anatomical and physiological dead spaces are identical But in some diseases, physiological dead space is more than anatomical dead space This is all about ventilation and dead spaces. If you found this video helpful, please share it with your friends too. And don’t forget to subscribe because lots more to come! Thanks for watching. See you in next video